What is Scaling?
In software systems, scaling is the act of increasing application resources to handle increased load.
Vertical Scaling
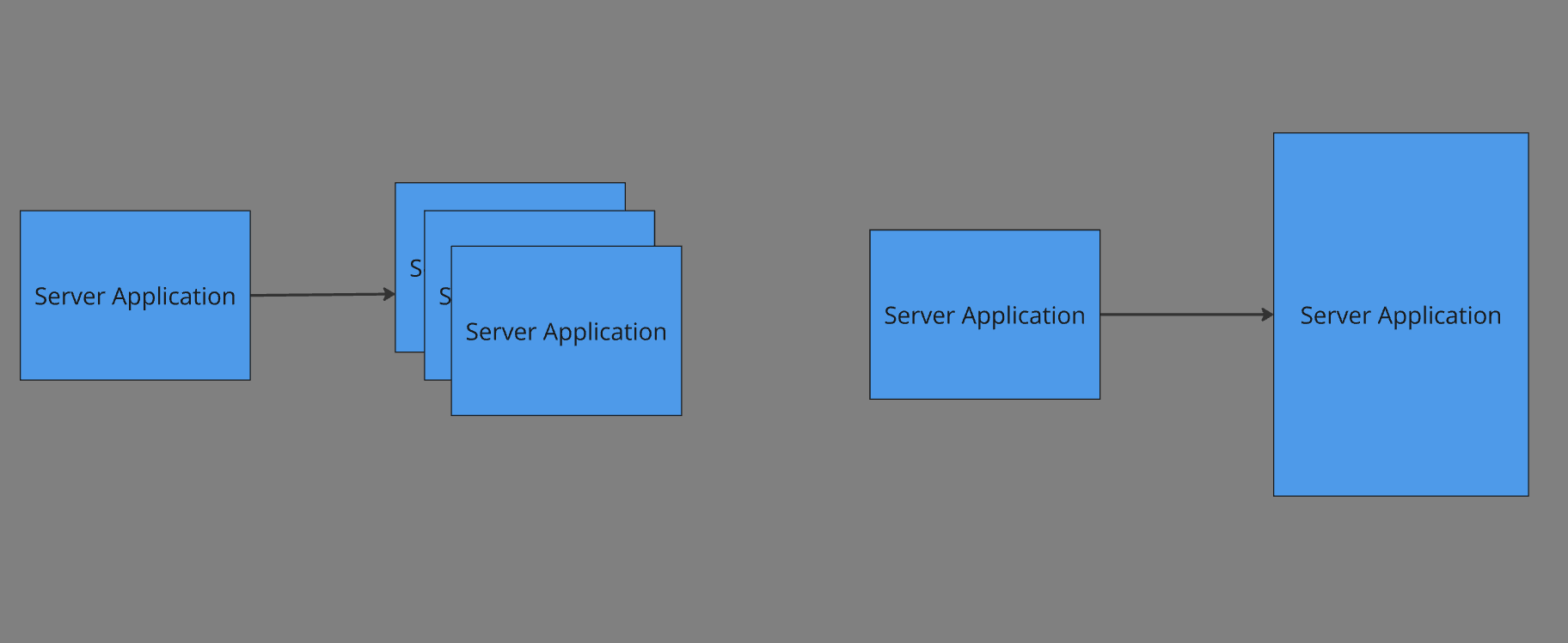
Vertical Scaling is the act of increasing the resources of a single server so it can handle more requests. This means increasing the RAM and CPU resources for a server.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal Scaling is the act of adding more application servers to handle increased load.
What Strategy Should You Use?
Most modern systems use a combination of horizontal and vertical scaling to handle increased system load.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Vertical Scaling
Pros
- Low in complexity. To scale an application vertically, one usually just needs to modify the values for CPU and RAM allocation.
Cons
- Does not scale as well as horizontal scaling.
- Using a single server introduces a single point of failure.
Horizontal Scaling
Pros
- Better at handling very large amounts of requests.
- Increased fault tolerance because we have multiple instances of a server running. If one goes down, another can handle requests in its place.
Cons
- High in complexity. Requires software like Kubernetes to manage the deployment of several application instances.
- Requires a load balancer to balance request volume across all server instances.
- Allows for multiple application instances to access the same data stores, introducing challenges with data access control and consistency in distributed systems.
- More expensive in terms of infrastructure costs.
Key Takeaways
- Vertical scaling increases the resources of a single server to handle increased load.
- Horizontal scaling increases the number of servers to handle increased load.
- Vertical scaling is typically easier and less expensive than horizontal scaling.
- Horizontal scaling is operationally more expensive and complex to implement than vertical scaling, but offers increased guarantees of scalability and fault tolerance.
